Since the founding our vision has been:
Transforming powerful AI capabilities into elegantly, simple features.
With a lot of buzz surrounding GenAI and the cool applications people are creating with it, I wanted to revisit some of the basics of GenAI. In other words, here are a few things you should know to appear knowledgeable in front of a GenAI expert.

This newsletter aims to demystify GenAI basics, providing you with essential knowledge to navigate this exciting field. As GenAI advancements continue at a remarkable pace, grasping these foundational concepts will help you better appreciate its potential applications and limitations.
Here are 5 things you should know about GenAI
1. What is GenAI? How It Differs from Traditional AI
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can create new content, whether that's text, images, code, or other types of data. Unlike traditional AI systems that primarily analyze and classify existing information, GenAI can generate entirely new outputs that didn't previously exist. This creative capability has captured widespread attention and opened up possibilities that were once in the realm of science fiction.
Key Differences from Traditional AI

Traditional AI relies heavily on explicit rules defined by human programmers and works best with structured data in well-defined scenarios. These systems follow deterministic decision-making processes and require manual updates when rules or scenarios change. In contrast, GenAI learns from data and adapts its behavior based on patterns it discovers, making it significantly more flexible and autonomous.
Creative Potential
GenAI demonstrates a level of creativity that traditional AI systems simply cannot match. By learning patterns from existing data, GenAI can generate novel content that resembles human-created work while offering unique variations. This creative capacity has implications across numerous fields, from content creation and design to software development and scientific research.
2. What's an LLM? Understanding GPT and Large Language Models
Large Language Models Defined
Large Language Models are massive deep learning systems pre-trained on enormous text datasets. They utilize transformer neural networks consisting of encoders and decoders with self-attention capabilities that allow them to understand relationships between words and phrases in sequences of text. This architecture enables LLMs to comprehend grammar, language, and knowledge through self-learning processes3.
How LLMs Work
Unlike earlier recurrent neural networks that processed inputs sequentially, LLMs process entire sequences in parallel. This parallel processing allows data scientists to leverage GPUs for training, significantly reducing the time required to build these complex models. The transformer architecture also enables the development of very large models with hundreds of billions of parameters that can ingest massive amounts of data from sources like the internet, Common Crawl, and Wikipedia.
3. How to Build Applications with GenAI
For those just starting with GenAI application development, the simplest approach involves using an instruction-tuned foundation model with well-crafted prompts. This technique, known as prompt engineering, can be implemented through zero-shot learning (where the model generates predictions without specific examples) or few-shot learning (where the model is given a few examples to guide its response)

Leveraging Existing Platforms
Rather than building GenAI infrastructure from scratch, beginners can benefit from platforms like Lamatic.ai that provide comprehensive tools for building, testing, and deploying GenAI applications. These platforms offer managed GenAI stacks that eliminate the need to build and maintain integrations to various components like LangChain, vector databases, and logging systems.

4. GenAI System Building Blocks
Understanding the fundamental components of GenAI systems helps beginners conceptualize how these applications work and how they might build their own solutions.
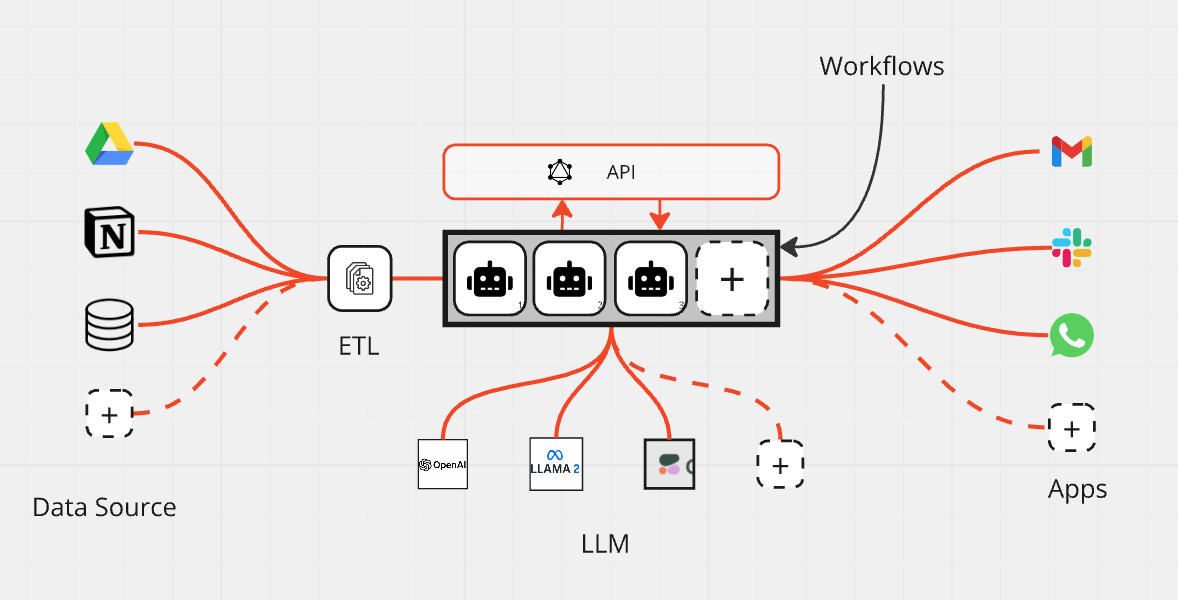
Foundation Models as the Core
At the center of most GenAI applications lies a foundation model, which serves as the core intelligence. This model can be accessed through an API provided by a model provider or self-hosted using open source or proprietary models. The foundation model selection depends on the specific requirements of your application and the type of content you aim to generate.
Essential Components
Beyond the foundation model, GenAI applications typically include several key components. Web or mobile applications provide the user interface, while APIs connect these interfaces to the foundation models. For more sophisticated applications using techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), text embedding endpoints and vector databases become necessary to store and retrieve context-relevant information.
Integration Capabilities
Modern GenAI platforms offer extensive integration capabilities that allow developers to connect models, applications, data sources, and agents to deliver use cases quickly. Lamatic.ai, for instance, provides integrations with various models and interfaces, making it easier to build comprehensive solutions without starting from scratch.
5. Continuously Improving Your GenAI System
GenAI systems are not static solutions but evolving platforms that benefit from ongoing refinement and enhancement.

Iterative Development and Refinement
Continuous improvement of GenAI systems often involves an iterative approach to refinement and optimization. When faced with complex challenges, professionals can leverage GenAI to generate and explore multiple solutions, enabling a wider range of possibilities. This rapid ideation process, followed by refinement through multiple iterations, not only speeds up the development cycle but also enhances the robustness and reliability of the resulting systems.
Data and Feedback Loops
Continuous improvement of GenAI systems relies heavily on effective feedback loops and data analysis. By monitoring system performance, analyzing user interactions, and collecting feedback, developers can identify areas for enhancement and prioritize improvements. This data-driven approach ensures that GenAI systems evolve to better meet user needs and adapt to changing requirements.
Conclusion: Your GenAI Journey
Understanding the basics of Generative AI provides a solid foundation for exploration and implementation in various contexts. From grasping the fundamental differences between traditional AI and GenAI to understanding LLMs, building applications, identifying core components, and implementing continuous improvement strategies, these five key areas offer beginners a comprehensive introduction to the field.
As you continue your GenAI journey, remember that the technology is evolving rapidly, with new capabilities and best practices emerging regularly. Platforms like Lamatic.ai offer tools and resources to help streamline development and deployment, allowing even beginners to create sophisticated GenAI applications. By starting with these fundamentals and gradually building your expertise, you'll be well-positioned to leverage GenAI's transformative potential in your personal and professional endeavors.


